Curcumin, a natural polyphenolic compound derived from the rhizomes of turmeric, has garnered significant attention due to its remarkable health benefits. A growing body of research demonstrates that curcumin possesses potent anti-inflammatory, antioxidant, lipid-lowering, and anti-tumor properties, and can effectively support cardiovascular and cerebrovascular health. However, despite its outstanding bioactivity, the clinical application of curcumin faces several challenges. Natural Field recognizes this issue and offers liposomal curcumin, an innovative product designed to address the low bioavailability of curcumin.
Curcumin and the Challenges It Faces
Curcumin is a polyphenolic compound typically extracted from the roots and stems of the turmeric plant. Extensive research has shown that curcumin has various biological activities, including lipid-lowering, anti-tumor, anti-inflammatory, and antioxidant functions. However, curcumin presents significant challenges for clinical application due to factors such as low water solubility, poor oral absorption, poor chemical stability, and rapid elimination and metabolism. The main reasons for these issues include: curcumin is poorly absorbed into the bloodstream through the gastrointestinal tract, with the maximum safe oral dose for adults being 12 g/d, yet the blood concentration at this dose only reaches 50 ng/ml. Animal studies have shown that curcumin's bioavailability is less than 1%[1]. (2) Curcumin has very low solubility in water (11 ng/mL)[2], and its unique molecular structure, characterized by high chemical reactivity, makes it highly sensitive to visible light and ultraviolet rays, leading to poor stability.
Why Liposomal Curcumin Works Better
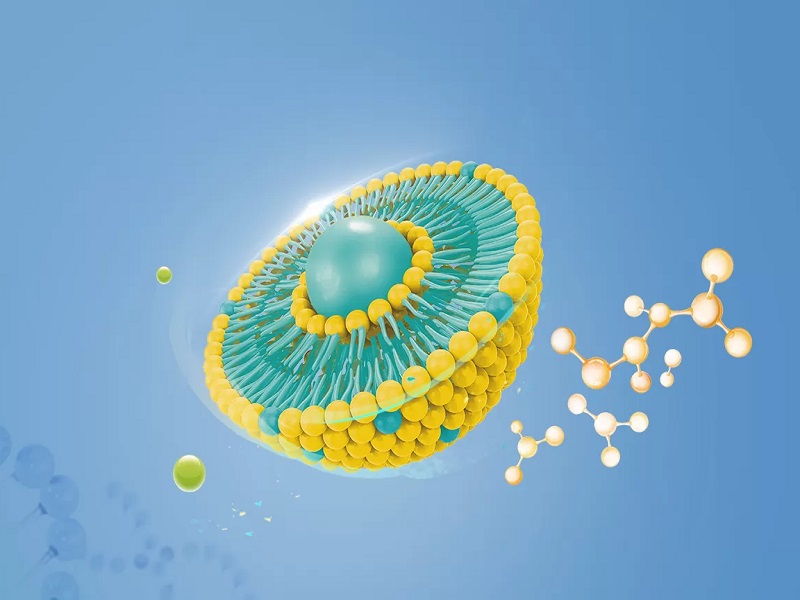
To address the issue of curcumin's low absorption, Natural Field has introduced liposomal encapsulation technology. Liposomal technology significantly enhances the bioavailability of curcumin, enabling it to perform excellently in applications such as functional beverages and gummies. The liposomal encapsulation technique involves enclosing curcumin in liposomes, which helps it be better absorbed by the human body and enhances its stability.
Advantages of Liposomal Technology
Biocompatibility and Biodegradability: The structure of liposomes closely resembles that of cell membranes, making them highly biocompatible and biodegradable. As a result, liposomes protect drugs from enzymatic degradation before they reach the targeted site. Additionally, by physically encapsulating the drug within the liposome, the drug's stability is improved, its toxicity is reduced, and higher dosages can be delivered, leading to better therapeutic effects.
Targeted Delivery: The bilayer surface formed by amphiphilic phospholipids can be chemically or physically modified with ligands or other functional groups, which gives the liposomes tissue-targeting properties. This modification allows the liposomes to extend their residence time at the target site and can even enable efficient targeted drug delivery.
Enhanced Drug Delivery for Nucleic Acids: By altering the surface charge of the bilayer, liposomes can be used to encapsulate and deliver DNA or RNA-based drugs, such as with cationic liposomes.
As a natural health ingredient, curcumin has great therapeutic potential, but its low bioavailability and instability have significantly limited the effectiveness of traditional curcumin products. Liposomal curcumin from Natural Field, through the application of liposomal technology, successfully addresses these issues, significantly improving curcumin’s absorption efficiency and stability. Liposomal curcumin not only enhances the bioavailability of curcumin but also protects it from digestive enzyme breakdown, ensuring it delivers maximum effectiveness. With the continued development of liposomal technology, liposomal curcumin will become the best choice for improving health and supporting bodily functions, especially in modern applications such as functional beverages, gummies, and more.
[1] Ruxin Chang, Liran Chen, Muhammad Qamar et al. The bioavailability, metabolism and microbial modulation of curcumin-loaded nanodelivery systems[J]. Advances in Colloid and Interface Science, 2023, 318.
[2] Yildiz D, Aydogmus Z, Senkal F, et al. Investigation of curcumin water solubility through emulsifying with biocompatible polyethylene glycol-based polymers[J]. Food Anal Methods, 2019, 12 (10): 2129-2138.

 EN
EN