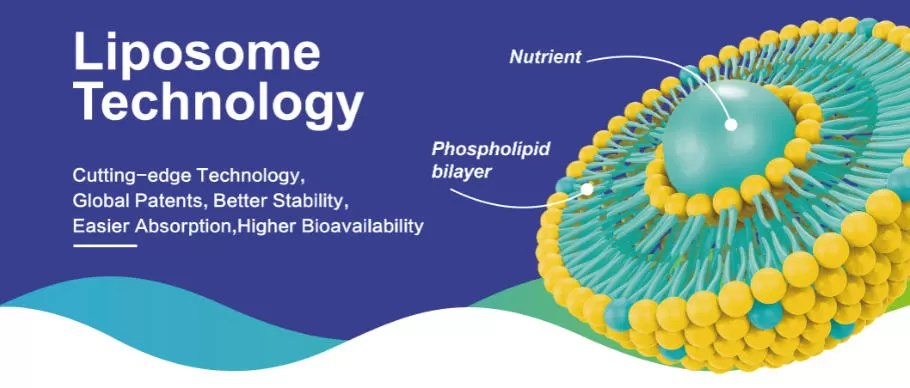
Turmeric is the plant in which Curcumin is extracted. Turmeric root contains only 2-5% Curcumin, so to receive the same amount of Curcumin as one serving of our Liposomal Curcumin, you’d need to consume a considerable amount every single day. In addition, it wouldn’t have the vastly increased bioavailability as our liposomal delivery provides.
Click to know more about Curcumin Powder vs Turmeric Powder.
 EN
EN
 es
es  jp
jp  ko
ko  fr
fr  de
de  it
it  ru
ru  pt
pt  th
th  ar
ar  ms
ms